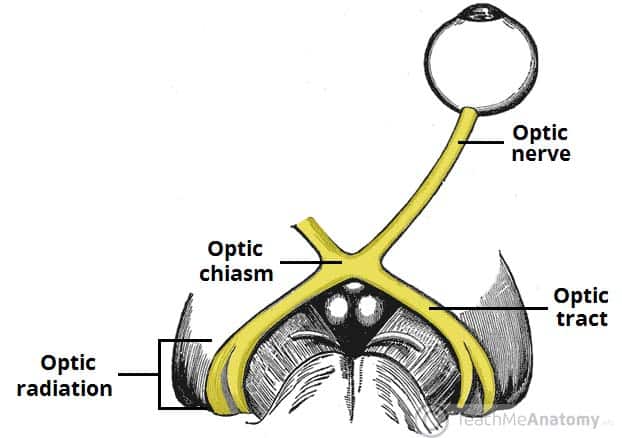
Dec 16, 2022The Optic Nerve (CN II) and Visual Pathway. The optic nerve (CN II) is the second cranial nerve, responsible for transmitting the special sensory information for vision. It is developed from the optic vesicle , an outpocketing of the forebrain. The optic nerve can therefore be considered part of the central nervous system, and examination of
The Optic Nerve – Visual Pathway – Chiasm – Tract – TeachMeAnatomy
The visual pathway consists of the series of cells and synapses that carry visual information from the environment to the brain for processing. It includes the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), optic radiations, and striate cortex ( Figure 13-1 ). The first cell in the pathway—a special sensory

Source Image: medicoapps.org
Download Image
Dec 19, 2022Visual stimuli from our surroundings are processed by an intricate system of interconnecting neurons, which begins with the optic nerve in the eye up to the visual processing center in our forebrain called the visual cortex. All the information travels in the form of nerve impulses that are triggered by photosensitive chemical reactions occurring in the retina. Several separate and parallel
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/8844/hRRfwPWCmuXu8amAUpzVVg_optic_radiation.png)
Source Image: kenhub.com
Download Image
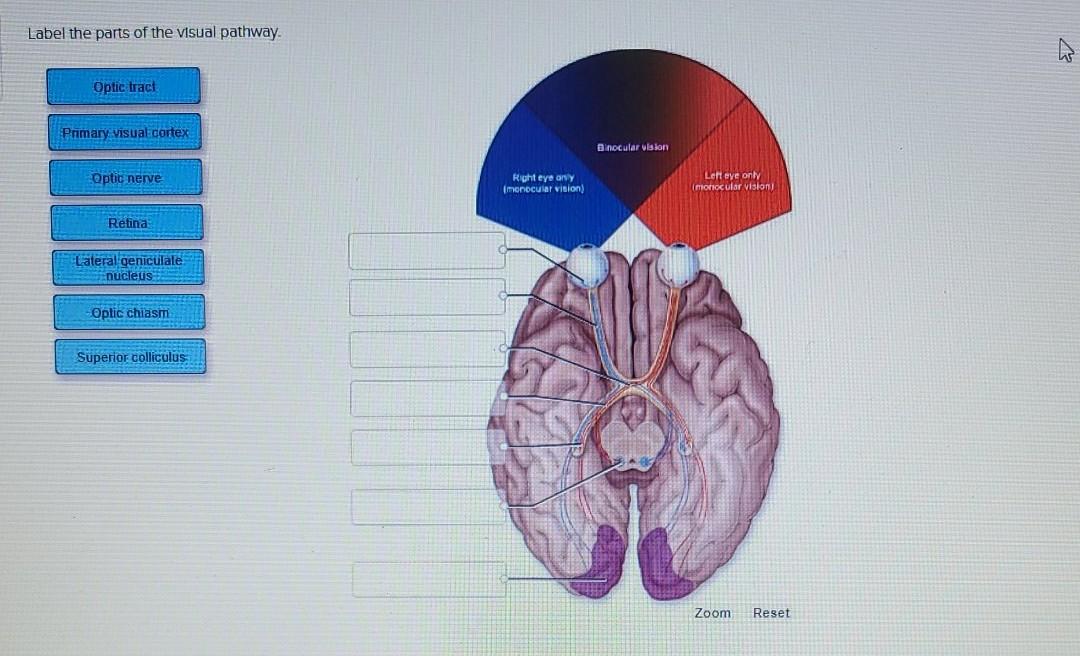
Solved Label the parts of the visual pathway. Optic tract | Chegg.com The visual pathway describes the anatomical pathway by which electrical signals generated by the retina are sent to the brain (Fig. 6).The nerve fibers of the retina, representing the axons of the ganglion cells, collect together at the optic disk before passing out of the eye through the orbital bones and into the brain via the optic nerve (the second cranial nerve).
![Active Learning in Machine Learning [Guide & Examples]](https://assets-global.website-files.com/5d7b77b063a9066d83e1209c/63b413cc43a073846453dca4_633a98dcd9b9793e1eebdfb6_HERO_Active%2520Learning%2520.png)
Source Image: v7labs.com
Download Image
Label The Parts Of The Visual Pathway
The visual pathway describes the anatomical pathway by which electrical signals generated by the retina are sent to the brain (Fig. 6).The nerve fibers of the retina, representing the axons of the ganglion cells, collect together at the optic disk before passing out of the eye through the orbital bones and into the brain via the optic nerve (the second cranial nerve). Aug 23, 2023The optic tract is a large bundle of nerve fibers of the visual pathway. It is a paired structure located in both left and right sides of the brain. The origin of the optic tract is the optic chiasm, an X-shaped structure located just above the pituitary gland (or hypophysis), in which optic nerve fibers partly decussate (meaning they cross to the other side, intersecting one another).
Active Learning in Machine Learning [Guide & Examples]
Visual cortex: This is where images received from your retina begin to get processed. The visual cortex has six layers and is the very beginning of your brain’s process of interpreting and recognizing what you see. Within these layers, depth perception is processed, and form, color, and motion are perceived. Visual pathway
Source Image: gmch.gov.in
Download Image
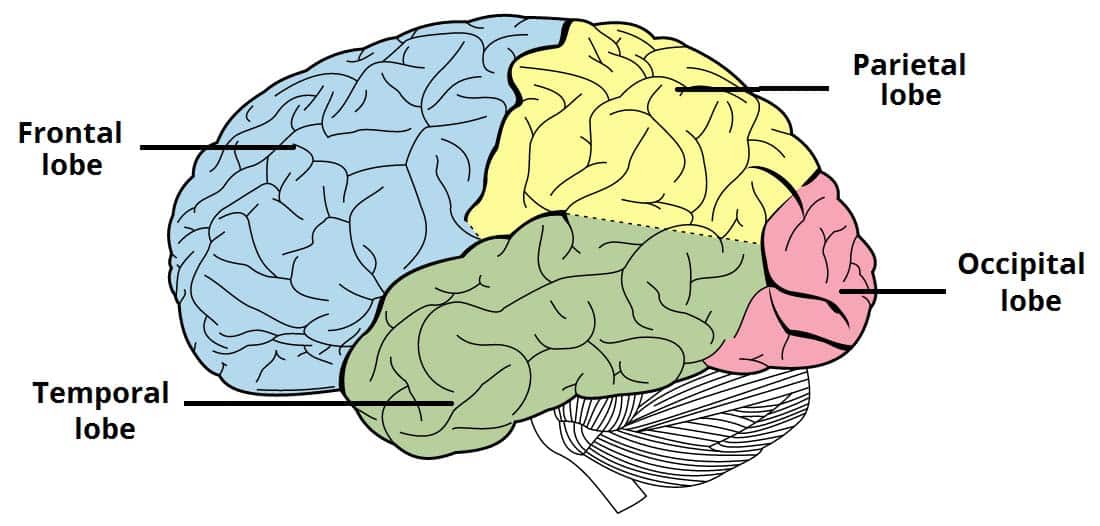
The Cerebrum – Lobes – Vasculature – TeachMeAnatomy Visual cortex: This is where images received from your retina begin to get processed. The visual cortex has six layers and is the very beginning of your brain’s process of interpreting and recognizing what you see. Within these layers, depth perception is processed, and form, color, and motion are perceived.
Source Image: teachmeanatomy.info
Download Image
The Optic Nerve – Visual Pathway – Chiasm – Tract – TeachMeAnatomy Dec 16, 2022The Optic Nerve (CN II) and Visual Pathway. The optic nerve (CN II) is the second cranial nerve, responsible for transmitting the special sensory information for vision. It is developed from the optic vesicle , an outpocketing of the forebrain. The optic nerve can therefore be considered part of the central nervous system, and examination of
Source Image: teachmeanatomy.info
Download Image
Solved Label the parts of the visual pathway. Optic tract | Chegg.com Dec 19, 2022Visual stimuli from our surroundings are processed by an intricate system of interconnecting neurons, which begins with the optic nerve in the eye up to the visual processing center in our forebrain called the visual cortex. All the information travels in the form of nerve impulses that are triggered by photosensitive chemical reactions occurring in the retina. Several separate and parallel
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Visual Pathway – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The visual pathway comprises the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic radiations, and the visual centre in the occipital lobe. Optic nerve lesions tend to cause ipsilateral monocular blindness. At the optic chiasm, fibres from the nasal half of the retina, corresponding to the temporal visual field, decussate.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Visual pathway (lecture 13) Diagram | Quizlet The visual pathway describes the anatomical pathway by which electrical signals generated by the retina are sent to the brain (Fig. 6).The nerve fibers of the retina, representing the axons of the ganglion cells, collect together at the optic disk before passing out of the eye through the orbital bones and into the brain via the optic nerve (the second cranial nerve).

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
The Dorsal Visual Pathway Represents Object-Centered Spatial Relations for Object Recognition | Journal of Neuroscience Aug 23, 2023The optic tract is a large bundle of nerve fibers of the visual pathway. It is a paired structure located in both left and right sides of the brain. The origin of the optic tract is the optic chiasm, an X-shaped structure located just above the pituitary gland (or hypophysis), in which optic nerve fibers partly decussate (meaning they cross to the other side, intersecting one another).

Source Image: jneurosci.org
Download Image
The Cerebrum – Lobes – Vasculature – TeachMeAnatomy
The Dorsal Visual Pathway Represents Object-Centered Spatial Relations for Object Recognition | Journal of Neuroscience The visual pathway consists of the series of cells and synapses that carry visual information from the environment to the brain for processing. It includes the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), optic radiations, and striate cortex ( Figure 13-1 ). The first cell in the pathway—a special sensory
Solved Label the parts of the visual pathway. Optic tract | Chegg.com Visual pathway (lecture 13) Diagram | Quizlet The visual pathway comprises the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic radiations, and the visual centre in the occipital lobe. Optic nerve lesions tend to cause ipsilateral monocular blindness. At the optic chiasm, fibres from the nasal half of the retina, corresponding to the temporal visual field, decussate.